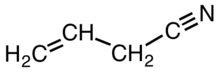
Allyl cyanide
[6] Allyl cyanide is produced in cruciferous vegetables by myrosinase, an enzyme which hydrolyses glucosinolates to form nitriles and other products.
[9] As cruciferous vegetables like cabbage, broccoli, cauliflower and sprouts are part of the human diet, allyl cyanide is normally consumed orally.
Although the dose-response relationship is still to be examined, it is therefore thought that allyl cyanide has no potency as a neurotoxicant when consumed in vegetables.
[10] Studies performed on rats showed that allyl cyanide cause loss of hair cells in the auditory system and troubling of the cornea.
[11] The same study also showed that the rearing activity of rats was reduced by oral ingestion of allyl cyanide.
[12] Studies done with mice showed that a single (albeit rather high) dose of allyl cyanide can cause permanent behavioural changes.
[17] Ataxia, trembling, convulsions, diarrhea, salivation, lacrimation and irregular breathing are known effects that are caused by oral ingestion of allyl cyanide.