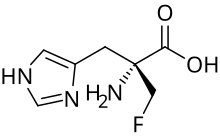
α-Fluoromethylhistidine
[1] It functions by forming a covalent linkage with a catalytic serine residue on the active site of HDC.
Due to its efficacy in reducing histamine levels in tissue mast cells, it has many applications in the study of histaminergic systems.
[3][4][5] In the central nervous systems of rats, α-FMH administration has been shown to cause impairments in long-term memory and learning.
A proposed mechanism involves the enhanced expression of neuropeptide Y (NPY) rather than HDC inhibition.
Due to the role of GSTs in detoxification, the efficacy of HDC inhibition by α-FMH in humans and its potential for the treatment of pathological conditions is subject to further research.