Back pain
[3] Diseases and inflammation of the gallbladder, pancreas, aorta and kidneys may also cause referred pain in the back.
[7] In most cases of herniated disks and stenosis, rest, injections or surgery have similar general pain-resolution outcomes on average after one year.
In the United States, acute low back pain is the fifth most common reason for physician visits and causes 40% of missed work days.
[19][21] A 2002 study found that lifestyle factors such as night-shift work and lack of physical activity can also increase the risk of lumbar disc disease.
[22] Severe spinal-cord compression is considered a surgical emergency and requires decompression to preserve motor and sensory function.
Spinal stenosis can occur in cases of severe spondylosis, spondylotheisis and age-associated thickening of the ligamentum flavum.
Neurogenic claudication can occur in cases of severe lumbar spinal stenosis and presents with symptoms of pain in the lower back, buttock or leg that is worsened by standing and relieved by sitting.
Vertebral compression fractures occur in four percent of patients presenting with lower back pain.
Metastasis to the bone also increases the risk of spinal-cord compression or vertebral fractures that require emergency surgical treatment.
Ankylosing spondylitis is common in young men and presents with a range of possible symptoms such as uveitis, psoriasis and inflammatory bowel disease.
Disease processes that can present with back pain include pancreatitis, kidney stones, severe urinary tract infections and abdominal aortic aneurysms.
[10] Heavy lifting, obesity, sedentary lifestyle and lack of exercise can increase the risk of back pain.
[2] A few studies suggest that psychosocial factors such as work-related stress and dysfunctional family relationships may correlate more closely with back pain than do structural abnormalities revealed in X-rays and other medical imaging scans.
[29][30][31][32] Back pain physical effects can range from muscle aching to a shooting, burning, or stabbing sensation.
Both acute and chronic back pain can be associated with psychological distress in the form of anxiety (worries, stress) or depression (sadness, discouragement).
Psychological distress is a common reaction to the suffering aspects of acute back pain, even when symptoms are short-term and not medically serious.
The straight leg test is a maneuver used to determine the presence of lumbosacral radiculopathy, which occurs when there is irritation in the nerve root that causes neurologic symptoms such as numbness and tingling.
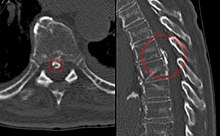
[36] Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is the preferred modality for the evaluation of back pain and visualization of bone, soft tissue, nerves and ligaments.
X-rays are a less costly initial option offered to patients with a low clinical suspicion of infection or malignancy, and they are combined with laboratory studies for interpretation.
[37] In cases of acute back pain, MRI is recommended for those with major risk factors or clinical suspicion of cancer, spinal infection or severe progressive neurological deficits.
[38] For patients with subacute to chronic back pain, MRI is recommended if minor risk factors exist for cancer, ankylosing spondylitis or vertebral compression fracture, or if significant trauma or symptomatic spinal stenosis is present.
[41][42] Laboratory testing may include white blood cell (WBC) count, erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), and C-reactive protein (CRP).
However, if there are certain "red flag" symptoms present, plain radiographs (X-ray), CT scan or magnetic resonance imaging may be recommended.
These red flags include:[43][11] Moderate-quality evidence exists that suggests that the combination of education and exercise may reduce an individual's risk of developing an episode of low back pain.
[75] If infection, such as a spinal epidural abscess, is the source of the back pain, surgery may be indicated when a trial of antibiotics is ineffective.
[79] Also, the hormone relaxin is released during pregnancy, which softens the structural tissues in the pelvis and lower back to prepare for vaginal delivery.
[79][77] Typical factors aggravating the back pain of pregnancy include standing, sitting, forward bending, lifting and walking.
[8][9] The American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons report approximately 12 million visits to doctor's offices each year are due to back pain.
[2] Missed work and disability related to low back pain costs over $50 billion each year in the United States.
[2] In the United Kingdom in 1998, approximately £1.6 billion per year was spent on expenses related to disability from back pain.