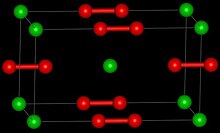
Barium peroxide
Barium peroxide is an inorganic compound with the formula BaO2.
This white solid (gray when impure) is one of the most common inorganic peroxides, and it was the first peroxide compound discovered.
Being an oxidizer and giving a vivid green colour upon ignition (as do all barium compounds), it finds some use in fireworks; historically, it was also used as a precursor for hydrogen peroxide.
[1] This reaction is the basis for the now-obsolete Brin process for separating oxygen from the atmosphere.
[4] In another obsolete application, barium peroxide was once used to produce hydrogen peroxide via its reaction with sulfuric acid:[3] The insoluble barium sulfate is filtered from the mixture.