Barium ferrate
[4] The ferrate(VI) anion is paramagnetic due to its two unpaired electrons and it has a tetrahedral molecular geometry.
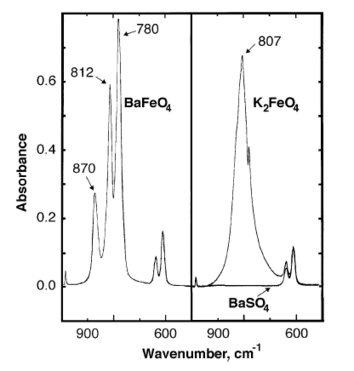
[3] X-ray diffraction has been used to determine the orthorhombic unit cell structure[1] (lattice vectors a ≠ b ≠ c, interaxial angles α=β=γ=90°)[5] of nanocrystalline BaFeO4.
[6] BaFeO4 follows the Curie–Weiss law and has a magnetic moment of (2.92 ± 0.03) × 10−23 A m2 (3.45 ± 0.1 BM) with a Weiss constant of −89 K.[8] Barium ferrate(VI) can be prepared by both wet and dry synthetic methods.
For example, the ferrate anion forms when a suitable iron salt is placed in alkaline conditions and a strong oxidising agent, such as sodium hypochlorite, is added.
[12] The purity of the product can be improved by carrying out the reaction at low temperature in the absence of carbon dioxide and by rapidly filtering and drying the precipitate, reducing the coprecipitation of barium hydroxide and barium carbonate as impurities.