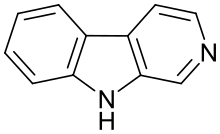
β-Carboline
[8][9] A synthetic derivative, 9-methyl-β-carboline, has shown neuroprotective effects including increased expression of neurotrophic factors and enhanced respiratory chain activity.
[10][11] This derivative has also been shown to enhance cognitive function,[12] increase dopaminergic neuron count and facilitate synaptic and dendritic proliferation.
[17][18] Specifically, expression of biosynthetic genes is facilitated by binding of the β-carboline to a large ATP-binding regulator of the LuxR family.
secretes a β-carboline (1-acetyl-β-carboline) preventing the pathogenic fungus Candida albicans to change to a more virulent growth form (yeast-to-filament transition).
For example, Louis Lewin, a prominent pharmacologist, demonstrated a dramatic benefit in neurological impairments after injections of B. caapi in patients with postencephalitic Parkinsonism.
In-vivo and rodent studies have shown that extracts of Banisteriopsis caapi and also Peganum harmala lead to striatal dopamine release.
[25] Since harmine also antagonizes N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) receptors,[26] some researchers speculatively attributed the rapid improvement in patients with Parkinson's disease to these antiglutamatergic effects.
Some β-carbolines, notably tetrahydro-β-carbolines, may be formed naturally in plants and the human body with tryptophan, serotonin and tryptamine as precursors.