Binary decision
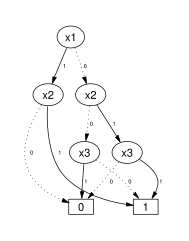
Examples include: A binary decision diagram (BDD) is a way to visually represent a boolean function.
One application of BDDs is in CAD software and digital circuit analysis where they are an efficient way to represent and manipulate boolean functions.
[6] The value of a boolean function can be determined by following a path in its BDD down to a terminal, making a binary decision at each node where a solid line is followed if the value of the variable at the node is true and a dotted line if it is false.
A BDD is said to be 'reduced' if the two following conditions are true: BDDs that are ordered and reduced can be called Reduced Ordered Binary Decision Diagrams (ROBDD).
In computer science, conditional statements are used to make binary decisions.
[9] A program can perform different computations or actions depending on whether a certain boolean value evaluates to true or false.
The if-then-else construct is a control flow statement which runs one of two code blocks depending on the value of a boolean expression, and its structure looks like this:The conditional expression is condition, and if it is true, then code block 1 is executed, otherwise code block 2 is executed.
It is also possible to combine multiple conditions with the else-if construct: This can be represented by the flow diagram on the right.
If one condition is found to be true, then the rest are skipped, so only one of the three code blocks above can be executed.
A while loop is a control flow statement which executes a code block repeatedly until its boolean expression becomes false, making a decision on whether to continue repeating before each loop.
This is similar to the if-then construct, but it can executing a code block multiple times.
You can help Wikipedia by expanding it.This mathematical logic-related article is a stub.

else if
