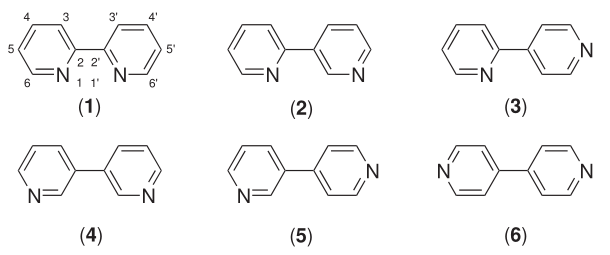
Bipyridine
Bipyridines are a family of organic compounds with the formula (C5H4N)2, consisting of two pyridyl (C5H4N) rings.
Its complexes are used in studies of electron and energy transfer, supramolecular, and materials chemistry, and catalysis.
This species is redox active, and its toxicity arises from its ability to interrupt biological electron transfer processes.
The 3,4′-bipyridine derivatives inamrinone and milrinone are used occasionally for short term treatment of congestive heart failure.
They inhibit phosphodiesterase and thus increasing cAMP, exerting positive inotropy and causing vasodilation.