Blood type
These antigens may be proteins, carbohydrates, glycoproteins, or glycolipids, depending on the blood group system.
[9]For another example, Von Willebrand disease may be more severe or apparent in people with blood type O.
For example, people with blood type O may be less susceptible to pro-thrombotic events induced by COVID-19 or long covid.
[10][11] Another example being the resistance to specific malaria species seen in individuals lacking the Duffy antigen.
[12] The Duffy antigen, presumably as a result of natural selection, is less common in population groups from areas having a high incidence of malaria.
Thus, transfusion can be considered safe as long as the serum of the recipient does not contain antibodies for the blood cell antigens of the donor.
It has been hypothesized that ABO IgM antibodies are produced in the first years of life by sensitization to environmental substances such as food, bacteria, and viruses, although blood group compatibility rules are applied to newborn and infants as a matter of practice.
[20] As with many other genetic traits, the distribution of ABO and Rh blood groups varies significantly between populations.
Across the world, blood products must be prescribed by a medical doctor (licensed physician or surgeon) in a similar way as medicines.
If a unit of incompatible blood is transfused between a donor and recipient, a severe acute hemolytic reaction with hemolysis (RBC destruction), kidney failure and shock is likely to occur, and death is a possibility.
[27] Antibodies can be highly active and can attack RBCs and bind components of the complement system to cause massive hemolysis of the transfused blood.
Frontline German Waffen-SS had blood group tattoos during World War II.
[33] One of the major advances of twentieth century medicine was to prevent this disease by stopping the formation of Anti-D antibodies by D negative mothers with an injectable medication called Rho(D) immune globulin.
FFP is quick-frozen to retain the labile clotting factors V and VIII, which are usually administered to patients who have a potentially fatal clotting problem caused by a condition such as advanced liver disease, overdose of anticoagulant, or disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC).
Clotting factors synthesized by modern recombinant methods are now in routine clinical use for hemophilia, as the risks of infection transmission that occur with pooled blood products are avoided.
An Rh D-negative patient who does not have any anti-D antibodies (never being previously sensitized to D-positive RBCs) can receive a transfusion of D-positive blood once, but this would cause sensitization to the D antigen, and a female patient would become at risk for hemolytic disease of the newborn.
If a D-negative patient has developed anti-D antibodies, a subsequent exposure to D-positive blood would lead to a potentially dangerous transfusion reaction.
In general, while the plasma fraction of a blood transfusion may carry donor antibodies not found in the recipient, a significant reaction is unlikely because of dilution.
Additionally, red blood cell surface antigens other than A, B and Rh D, might cause adverse reactions and sensitization, if they can bind to the corresponding antibodies to generate an immune response.
Conversely, AB plasma can be given to patients of any ABO blood group, because it does not contain any anti-A or anti-B antibodies.
It remains to be seen whether this appearance is related to inborn differences between individuals or it is the result of some damage of bacterial kind.
[47] This was the discovery of blood groups for which Landsteiner was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1930.
[49][50] Thus, after Landsteiner, three blood types were initially recognised, namely A, B, and C.[50] Czech serologist Jan Janský was the first to recognise and designate four blood types in 1907 that he published in a local journal,[51] using the Roman numerical I, II, III, and IV (corresponding to modern O, A, B, and AB respectively).
Moss's system was adopted in Britain, France, and the US, while Janský's was preferred in most other European countries and some parts of the US.
[57] In 1927, Landsteiner, who had moved to the Rockefeller Institute for Medical Research in New York, and as a member of a committee of the National Research Council concerned with blood grouping suggested to substitute Janský's and Moss's systems with the letters O, A, B, and AB, first introduced by Polish physician Ludwik Hirszfeld and German physician Emil von Dungern.
In 1928 the Permanent Commission on Biological Standardization adopted Landsteiner's proposal and stated:The Commission learns with satisfaction that, on the initiative of the Health Organization of the League of Nations, the nomenclature proposed by von Dungern and Hirszfeld for the classification of blood groups has been generally accepted, and recommends that this nomenclature shall be adopted for international use as follows: 0 A B AB.
To facilitate the change from the nomenclature hitherto employed the following is suggested: This classification became widely accepted and after the early 1950s it was universally followed.
[62] Hirszfeld and Dungern discovered the inheritance of blood types as Mendelian genetics in 1910 and the existence of sub-types of A in 1911.
[65] Development of the Coombs test in 1945,[66] the advent of transfusion medicine, and the understanding of ABO hemolytic disease of the newborn led to discovery of more blood groups.




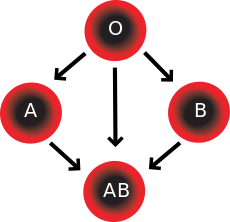
In addition to donating to the same blood group; type O blood donors can give to A, B and AB; blood donors of types A and B can give to AB.
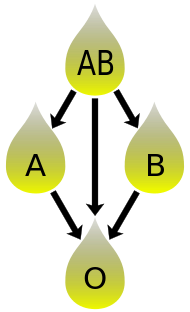
In addition to donating to the same blood group; plasma from type AB can be given to A, B and O; plasma from types A, B and AB can be given to O.
