Brodmann area
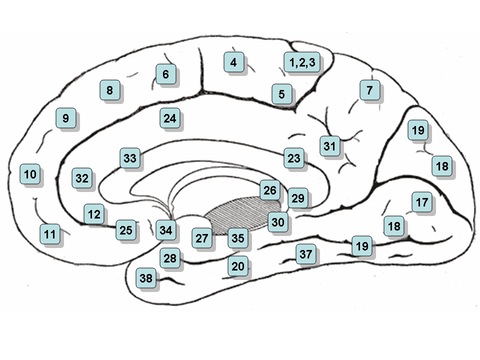
A Brodmann area is a region of the cerebral cortex, in the human or other primate brain, defined by its cytoarchitecture, or histological structure and organization of cells.
Brodmann mapped the human brain based on the varied cellular structure across the cortex and identified 52 distinct regions, which he numbered 1 to 52.
Brodmann published his maps of cortical areas in humans, monkeys, and other species in 1909,[2] along with many other findings and observations regarding the general cell types and laminar organization of the mammalian cortex.
[4] Brodmann areas have been discussed, debated, refined, and renamed exhaustively for nearly a century and remain the most widely known and frequently cited cytoarchitectural organization of the human cortex.
A simple example of this type of correspondence is the primary motor cortex, a strip of tissue running along the anterior edge of the central sulcus.
This "somatotopic" representation is not evenly distributed, however; the head, for example, is represented by a region about three times as large as the zone for the entire back and trunk.
The maps for visual areas are retinotopic, meaning that they reflect the topography of the retina: the layer of light-activated neurons lining the back of the eye.
[7] When von Bonin and Bailey constructed a brain map for the macaque monkey, they found the description of Brodmann inadequate and wrote: "Brodmann (1907), it is true, prepared a map of the human brain which has been widely reproduced, but, unfortunately, the data on which it was based was never published"[8] They instead used the cytoarchitectonic scheme of Constantin von Economo and Georg N. Koskinas published in 1925[4] which had the "only acceptable detailed description of the human cortex".