Bone fracture
Collagen's rubbery consistency allows bone fragments to move only a small amount unless severe or persistent force is applied.
[citation needed] At this stage, some of the fibroblasts begin to lay down bone matrix in the form of collagen monomers.
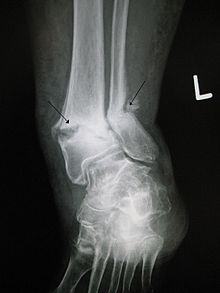
Healing bone callus on average is sufficiently mineralized to show up on X-ray within 6 weeks in adults and less in children.
Although there are theoretical concerns about NSAIDs slowing the rate of healing, there is not enough evidence to warrant withholding the use of this type analgesic in simple fractures.
[9] Smokers generally have lower bone density than non-smokers, so they have a much higher risk of fractures.
In situations where projectional radiography alone is insufficient, Computed Tomography (CT) or Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) may be indicated.
[citation needed] An anatomical classification may begin with specifying the involved body part, such as the head or arm, followed by more specific localization.
Preventive measures depend to some extent on the specific sport, but learning proper technique, wearing protective gear and having a realistic estimation of one's own capabilities and limitations can all help reduce the risk of bone fracture.
In contact sports rules have been put in place to protect athlete health, such as the prohibition of unnecessary roughness in American football.
[34] Taking vibration therapy can also help strengthening bones and reducing the risk of a fracture.
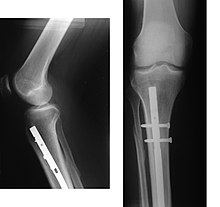
If being treated with surgery, surgical nails, screws, plates, and wires are used to hold the fractured bone together more directly.
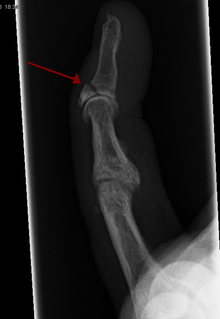
A device called a Suzuki frame may be used in cases of deep, complex intra-articular digit fractures.
[40] By allowing only limited movement, immobilization helps preserve anatomical alignment while enabling callus formation, toward the target of achieving union.
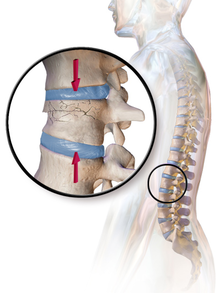
[42] With some fractures such as hip fractures (usually caused by osteoporosis), surgery is offered routinely because non-operative treatment results in prolonged immobilisation, which commonly results in complications including chest infections, pressure sores, deconditioning, deep vein thrombosis (DVT), and pulmonary embolism, which are more dangerous than surgery.
For this reason, open fractures and osteotomies call for very careful antiseptic procedures and prophylactic use of antibiotics.
Stress shielding occurs when plates or screws carry too large of a portion of the bone's load, causing atrophy.
The heat generated by the friction of installing hardware can accumulate easily and damage bone tissue, reducing the strength of the connections.
If dissimilar metals are installed in contact with one another (i.e., a titanium plate with cobalt-chromium alloy or stainless steel screws), galvanic corrosion will result.
Bone stimulation with either electromagnetic or ultrasound waves may be suggested as an alternative to surgery to reduce the healing time for non-union fractures.



(a) closed fracture
(b) open fracture
(c) transverse fracture
(d) spiral fracture
(e) comminuted fracture
(f) impacted fracture
(g) greenstick fracture
(h) oblique fracture