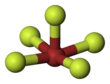
Bromine pentafluoride
Laser ablation of solid silicates in the presence of BrF5 releases O2 for subsequent analysis.
[2] It has also been tested as an oxidizer in liquid rocket propellants and is used as a fluorinating agent in the processing of uranium.
[3] This reaction is suitable for the preparation of large quantities,[citation needed] and is carried out at temperatures over 150 °C (302 °F) with an excess of fluorine: For the preparation of smaller amounts, potassium bromide is used:[3] This route yields BrF5 almost completely free of trifluorides and other impurities.
Its vapors are also extremely irritating to all parts of the human body, especially the skin, eyes and other mucous membranes.
[5] Additionally, BrF5 is a strong oxidizing agent and may spontaneously ignite or explode upon contact with flammable substances such as organic materials and metal dust.