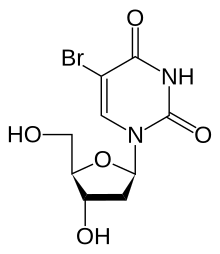
Bromodeoxyuridine
Bromodeoxyuridine (5-bromo-2'-deoxyuridine, BrdU, BUdR, BrdUrd, broxuridine) is a synthetic nucleoside analogue with a chemical structure similar to thymidine.
[citation needed] However, because it is neither radioactive nor myelotoxic at labeling concentrations, it is widely preferred for in vivo studies of cancer cell proliferation.
The Br atom acts as an anomalous scatterer and its larger size will affect the crystal's X-ray diffraction enough to detect isomorphous differences as well.
[14] Subsequent sequencing of the labeled DNA can then be used to identify the microbial taxa that participated in the degradation of the added carbon source.
However, it is not certain whether all microbes present in an environmental sample can incorporate BrdU into their biomass during de novo DNA synthesis.