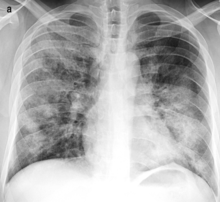
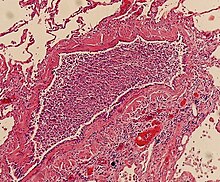
Bronchopneumonia
It is the acute inflammation of the bronchi, accompanied by inflamed patches in the nearby lobules of the lungs.
[1] It is often contrasted with lobar pneumonia; but, in clinical practice, the types are difficult to apply, as the patterns usually overlap.
On gross pathology there are typically multiple foci of consolidation present in the basal lobes of the human lung, often bilateral.
These lesions are 2–4 cm in diameter, grey-yellow, dry, often centered on a bronchiole, poorly delimited, and with the tendency to confluence, especially in children.
Light microscopy typically shows neutrophils in bronchi, bronchioles and adjacent alveolar spaces.