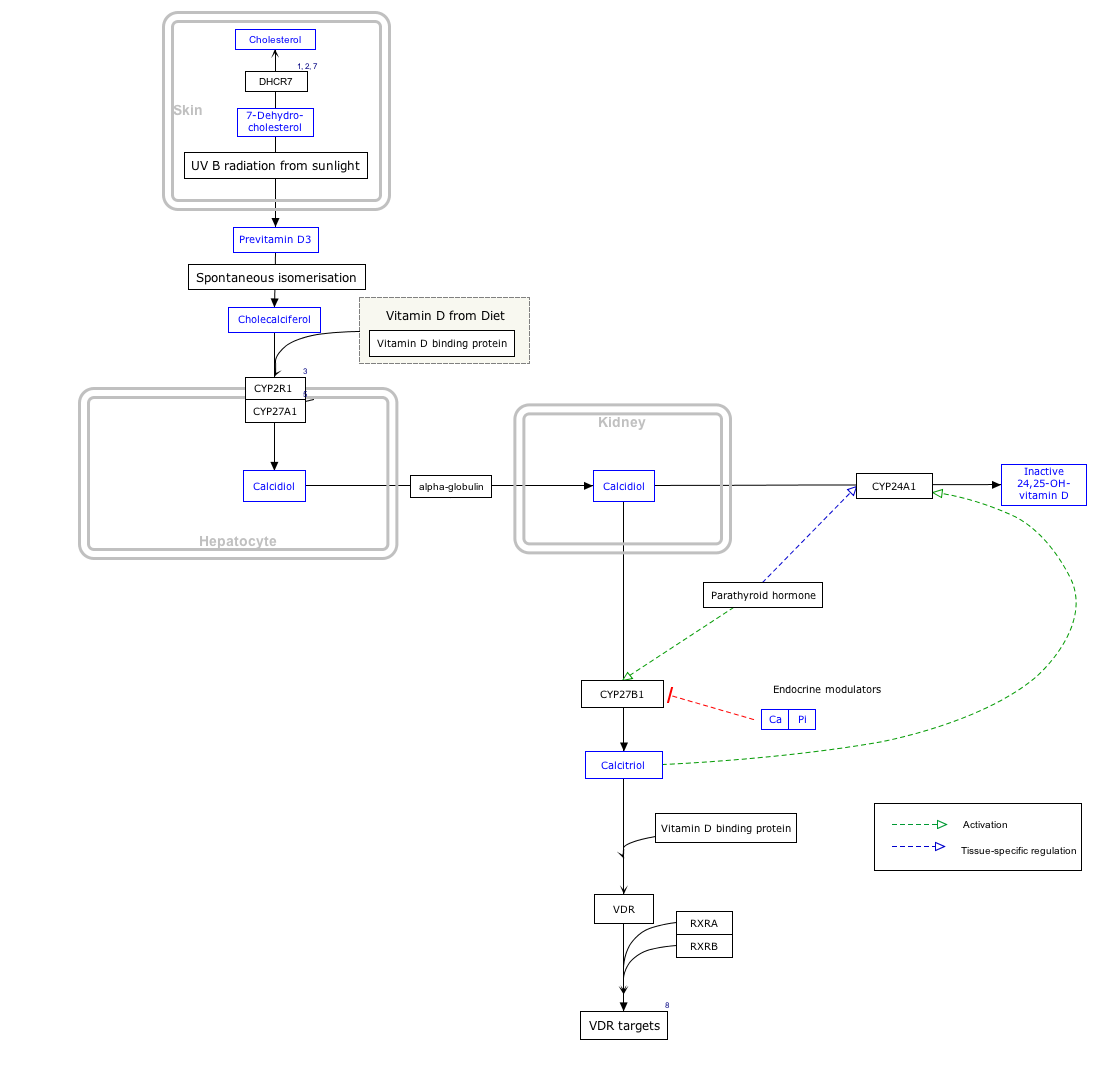
CYP24A1
[5][6] CYP24A1 was identified in the early 1970s and was first thought to be involved in vitamin D metabolism as the renal 25-hydroxyvitamin D3-24-hydroxylase, modifying calcifediol (25-hydroxyvitamin D) to produce 24,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol (24,25-dihydroxyvitamin D).
Subsequent studies using recombinant CYP24A1 showed that it could also catalyze multiple other hydroxylation reactions at the side chain carbons known as C-24 and C-23 in both 25-OH-D3 and the active hormonal form, 1,25-(OH)2D3.
[6] Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene.
[§ 1] CYP24A1 is expressed in tissues which are considered targets for vitamin D, including kidney, intestine and bone.
Through regulation of CYP24A1 expression, a negative feedback control system is created to limit the effects of 1,25-(OH)2D3.