Vitamin D
Vitamin D is a group of structurally related, fat-soluble compounds responsible for increasing intestinal absorption of calcium, magnesium, and phosphate, along with numerous other biological functions.
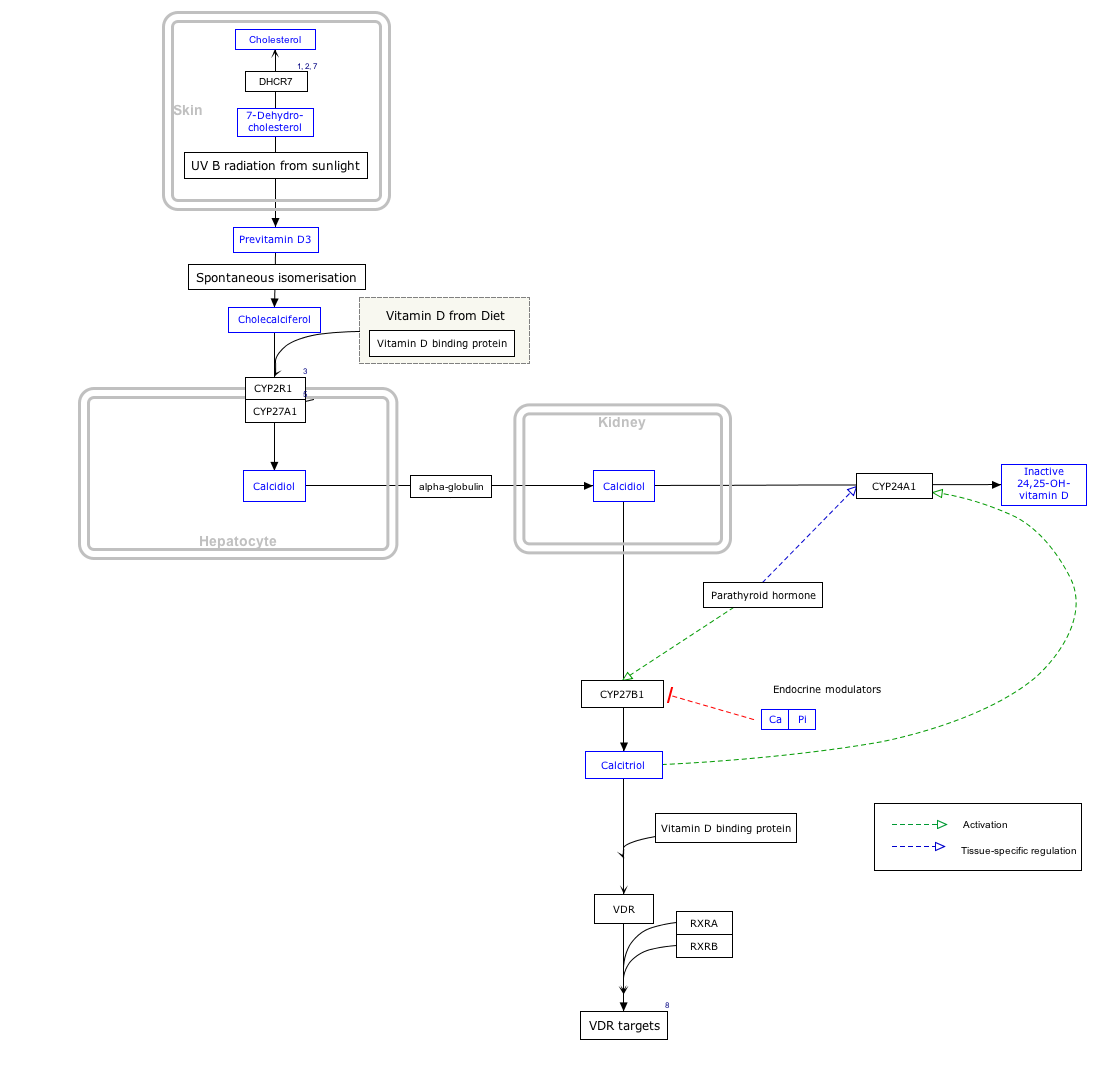
[1][13] When calcitriol binds to the VDR, it enables the receptor to act as a transcription factor, modulating the gene expression of transport proteins involved in calcium absorption in the intestine, such as TRPV6 and calbindin.
[32] Using the 25(OH)D assay as a screening tool of the generally healthy population to identify and treat individuals is considered not as cost-effective as a government mandated fortification program.
[24] Consumption of foods that naturally contain vitamin D is rarely sufficient to maintain recommended serum concentration of 25(OH)D in the absence of the contribution of skin synthesis.
[5][24] Organ transplant recipients receive immunosuppressive therapy that is associated with an increased risk to develop skin cancer, so they are advised to avoid sunlight exposure, and to take a vitamin D supplement.
[29][50][52] However, despite having on-average 25(OH)D serum contentrations below the 50 nmol/L amount considered sufficient, African Americans have higher bone mineral density and lower fracture risk when compared to European-origin people.
[54] The bone density and fracture risk paradox does not necessarily carry over to non-skeletal health conditions such as arterial calcification, cancer, diabetes or all-cause mortality.
[4]: 424–445 Per the revision: "UL is defined as "the highest average daily intake of a nutrient that is likely to pose no risk of adverse health effects for nearly all persons in the general population".
[4]: 124–299 Some researchers claim the IOM was too definitive in its recommendations and made a mathematical mistake when calculating the blood level of vitamin D associated with bone health.
[4]: 424–435 Rickets, a childhood disease, is characterized by impeded growth and soft, weak, deformed long bones that bend and bow under their weight as children start to walk.
[9] For older people with osteoporosis, taking vitamin D with calcium may help prevent hip fractures, but it also slightly increases the risk of stomach and kidney problems.
[113][114][115][116] Low plasma vitamin D concentrations have been reported for autoimmune thyroid diseases,[117] lupus,[118] myasthenia gravis,[119] rheumatoid arthritis,[120] and multiple sclerosis.
[128] Supplementation leads to improvements in scores for clinical inflammatory bowel disease activity and biochemical markers,[128][129] and less frequent relapse of symptoms in IBD.
"[131] Same year, the UK National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) position was to not recommend to offer a vitamin D supplement to people solely to prevent or treat COVID-19.
[134][135][136][137][138] Supplementation trials, mostly large, single, oral dose upon hospital admission, reported lower subsequent transfers to intensive care and to all-cause mortality.
[143] Another meta-analysis reported that vitamin D supplementation significantly improved glycemic control [homeostatic model assessment-insulin resistance (HOMA-IR)], hemoglobin A1C (HbA1C), and fasting blood glucose (FBG) in individuals with type 2 diabetes.
[149] A systematic review of clinical studies found an association between low vitamin D levels with cognitive impairment and a higher risk of developing Alzheimer's disease.
Part of the complexity is that vitamin D deficiency is also linked to morbidities that are associated with erectile dysfunction, such as obesity, hypertension, diabetes mellitus, hypercholesterolemia, chronic kidney disease and hypogonadism.
[172][173] The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) in 2016[58] reviewed the current evidence, finding the relationship between serum 25(OH)D concentration and musculoskeletal health outcomes is widely variable.
[185][186][187] Only circa 500 million years ago, when animals began to leave the oceans for land, did the UV-converted molecule take on an hormone function as a promoter of calcium regulation.
Unlike land-based vertebrates, large amounts of vitamin D3 are stored in the liver and fatty tissues, making fish a good dietary source for human consumption.
A long-term climate shift toward drier conditions promoted life-changes from sedentary forest-dwelling with a primarily plant-based diet toward upright walking/running on open terrain and more meat consumption.
[190][189][198] For people with low skin melanin, moderate sun exposure to the face, arms and lower legs several times a week is sufficient.
When synthesized by monocyte-macrophages, calcitriol acts locally as a cytokine, modulating body defenses against microbial invaders by stimulating the innate immune system.
[207] The VDR/RXR complex subsequently binds to vitamin D response elements (VDRE) which are specific DNA sequences adjacent to genes, numbers estimated as being in the thousands.
They play a significant role in immune function, cellular signaling, and even blood coagulation, demonstrating the broad impact of vitamin D regulated genes on human physiology.
[224] In northern European countries, cod liver oil had a long history of folklore medical uses, including applied to the skin and taken orally as a treatment for rheumatism and gout.
He recommended that the diets of the pregnant and nursing females and the weaned cubs be switched from lean horse meat to goat - including calcium- and phosphorus-containing bones - and cod liver oil, solving the problem.
[6] Edward Mellanby, a British researcher, observed that dogs that were fed cod liver oil did not develop rickets, and (wrongly) concluded that vitamin A could prevent the disease.
[6][7] Adolf Windaus, at the University of Göttingen in Germany, received the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1928 "...for the services rendered through his research into the constitution of the sterols and their connection with the vitamins.