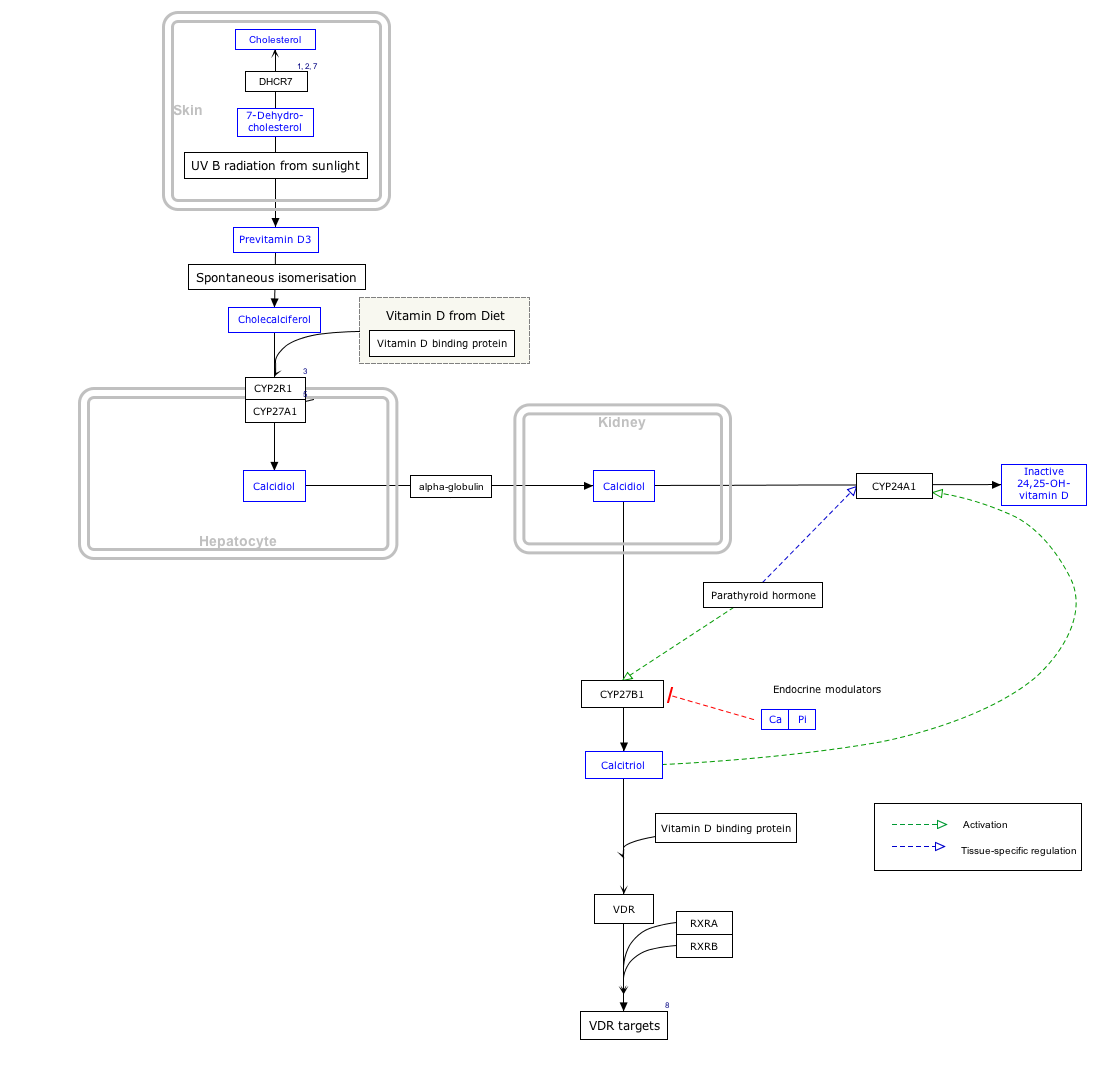
Vitamin D receptor
[7] VDR is expressed in most tissues of the body, and regulates transcription of genes involved in intestinal and renal transport of calcium and other minerals.
[14] VDR gene variants seem to influence many biological endpoints, including those related to osteoporosis [15] The vitamin D receptor plays an important role in regulating the hair cycle.
Researchers have focused their efforts in elucidating the role of VDR polymorphisms in different diseases and normal phenotypes such as the HIV-1 infection susceptibility and progression or the natural aging process.
The most remarkable findings include the report of VDR variants that bolster vitamin-D action and that are directly correlated with AIDS progression rates, that VDR association with progression to AIDS follows an additive model[11] and the role of FokI polymorphism as a risk factor for enveloped virus infection as revealed in a meta-analysis.
[12] Vitamin D receptor has been shown to interact with many other factors which will affect transcription activation: Click on genes, proteins and metabolites below to link to respective articles.