CT scan
The 1979 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine was awarded jointly to South African-American physicist Allan MacLeod Cormack and British electrical engineer Godfrey Hounsfield "for the development of computer-assisted tomography".
[10] This type had a major advantage since sweep speeds can be much faster, allowing for less blurry imaging of moving structures, such as the heart and arteries.
Several institutions offer full-body scans for the general population although this practice goes against the advice and official position of many professional organizations in the field primarily due to the radiation dose applied.
CT scanning of the head is also used in CT-guided stereotactic surgery and radiosurgery for treatment of intracranial tumors, arteriovenous malformations, and other surgically treatable conditions using a device known as the N-localizer.
For evaluation of chronic interstitial processes such as emphysema, and fibrosis,[42] thin sections with high spatial frequency reconstructions are used; often scans are performed both on inspiration and expiration.
[45] Perhaps persuaded by fear, patients and doctors sometimes agree to an intensive schedule of CT scans, sometimes up to every three months and beyond the recommended guidelines, in an attempt to do surveillance on the nodules.
For more complex anatomies and procedures, such as heart valve interventions, a true 3D reconstruction or a 3D print is created based on these CT images to gain a deeper understanding.
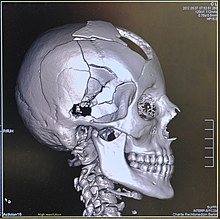
[70] For the axial skeleton and extremities, CT is often used to image complex fractures, especially ones around joints, because of its ability to reconstruct the area of interest in multiple planes.
Using CT scans, conservators and researchers are able to determine the material composition of the objects they are exploring, such as the position of ink along the layers of a scroll, without any additional harm.
These scans have been optimal for research focused on the workings of the Antikythera mechanism or the text hidden inside the charred outer layers of the En-Gedi Scroll.
[88] Micro-CT has also proved useful for analyzing more recent artifacts such as still-sealed historic correspondence that employed the technique of letterlocking (complex folding and cuts) that provided a "tamper-evident locking mechanism".
[92] Varied types of fungus can degrade wood to different degrees, one Belgium research group has been used X-ray CT 3 dimension with sub-micron resolution unveiled fungi can penetrate micropores of 0.6 μm[93] under certain conditions.
Sawmills use industrial CT scanners to detect round defects, for instance knots, to improve total value of timber productions.
Most sawmills are planning to incorporate this robust detection tool to improve productivity in the long run, however initial investment cost is high.
The epitomes of volume rendering models feature a mix of for example coloring and shading in order to create realistic and observable representations.
[103] The attenuation of metallic implants depends on the atomic number of the element used: Titanium usually has an amount of +1000 HU, iron steel can completely block the X-ray and is, therefore, responsible for well-known line-artifacts in computed tomograms.
Artifacts are caused by abrupt transitions between low- and high-density materials, which results in data values that exceed the dynamic range of the processing electronics.
However, increased dosage raises the adverse side effects, including the risk of radiation-induced cancer – a four-phase abdominal CT gives the same radiation dose as 300 chest X-rays.
[149] An Australian study of 10.9 million people reported that the increased incidence of cancer after CT scan exposure in this cohort was mostly due to irradiation.
Moreover, a highly significant finding that was previously unreported is that some patients received >100 mSv dose from CT scans in a single day,[158] which counteracts existing criticisms some investigators may have on the effects of protracted versus acute exposure.
[190][191][192] Most adverse health effects of radiation exposure may be grouped in two general categories: The added lifetime risk of developing cancer by a single abdominal CT of 8 mSv is estimated to be 0.05%, or 1 one in 2,000.
The IV line is established in case of contrast-enhanced CT. After selecting proper[clarification needed] and rate of contrast from the pressure injector, the scout is taken to localize and plan the scan.
The attenuation of metallic implants depends on the atomic number of the element used: Titanium usually has an amount of +1000 HU, iron steel can completely extinguish the X-ray and is, therefore, responsible for well-known line-artifacts in computed tomograms.
Artifacts are caused by abrupt transitions between low- and high-density materials, which results in data values that exceed the dynamic range of the processing electronics.
[210][211] In October 1963, William H. Oldendorf received a U.S. patent for a "radiant energy apparatus for investigating selected areas of interior objects obscured by dense material".
[224] This initiative has been endorsed and applied by a growing list of various professional medical organizations around the world and has received support and assistance from companies that manufacture equipment used in Radiology.
[225] The World Health Organization and International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) of the United Nations have also been working in this area and have ongoing projects designed to broaden best practices and lower patient radiation dose.
[29] An estimated 72 million scans were performed in the United States in 2007,[30] accounting for close to half of the total per-capita dose rate from radiologic and nuclear medicine procedures.
Shortening of the scanning time to around 1 second, eliminating the strict need for the subject to remain still or be sedated, is one of the main reasons for the large increase in the pediatric population (especially for the diagnosis of appendicitis).
[233][234] PCDs have only recently become feasible in CT scanners due to improvements in detector technologies that can cope with the volume and rate of data required.





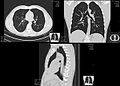

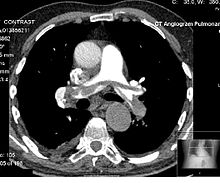


− Average intensity projection
− Maximum intensity projection
− Thin slice ( median plane )
− Volume rendering by high and low threshold for radiodensity

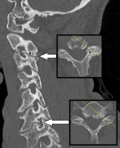

T: X-ray tube
D: X-ray detectors
X: X-ray beam
R: Gantry rotation
