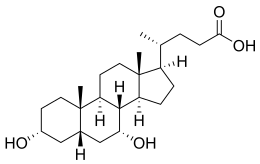
Chenodeoxycholic acid
[4] It occurs as a white crystalline substance insoluble in water but soluble in alcohol and acetic acid, with melting point at 165–167 °C.
This results in the conjugated bile acids being ionized at the usual pH in the intestine, and staying in the gastrointestinal tract until reaching the ileum to be reabsorbed.
[3] In the United States, chenodeoxycholic acid is indicated for people with radiolucent stones in well-opacifying gallbladders, in whom selective surgery would be undertaken except for the presence of increased surgical risk due to systemic disease or age.
[13] As diarrhea is frequent when CDCA is used in gallstone dissolution, it has been studied as a possible treatment for constipation and has been shown to accelerate colonic transit and improve bowel function.
[14] The Australian biotechnology company Giaconda has tested a treatment for hepatitis C infection that combines chenodeoxycholic acid with bezafibrate.