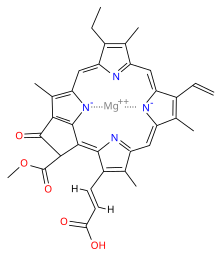
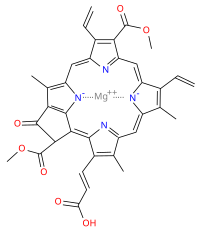
Chlorophyll c
[1][2][3] These pigments are characterized by their unusual chemical structure, with a porphyrin as opposed to the chlorin (which has a reduced ring D) as the core; they also do not have an isoprenoid tail.
Both these features stand out from the other chlorophylls commonly found in algae and plants.
[2] It has a blue-green color and is an accessory pigment, particularly significant in its absorption of light in the 447–520 nm wavelength region.
[3] Like chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b, it helps the organism gather light and passes a quanta of excitation energy through the light harvesting antennae to the photosynthetic reaction centre.
[8] The 171 oxidtion was proposed to proceed by "hydroxylation of the 17-propionate reside at the 171-position and successive dehydration to the 17-acrylate residue.