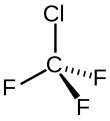
Chlorotrifluoromethane
Chlorotrifluoromethane, R-13, CFC-13, or Freon 13, is a non-flammable, non-corrosive, nontoxic chlorofluorocarbon (CFC) and also a mixed halomethane.
When released into the environment, CFC-13 has a high ozone depletion potential, and long atmospheric lifetime.
[5][6] It can be prepared by reacting carbon tetrachloride with hydrogen fluoride in the presence of a catalytic amount of antimony pentachloride: This reaction can also produce trichlorofluoromethane (CCl3F), dichlorodifluoromethane (CCl2F2) and tetrafluoromethane (CF4).
[5] CFC-13's ozone depletion potential (ODP) is high— 1[9] (CCl3F = 1)—it is categorized as a Class I in the IPCC's list of ozone-depleting substances.
[10] Contrary to the Montreal Protocol, the atmospheric emissions of CFC-13 and four other chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), increased between 2010 and 2020.