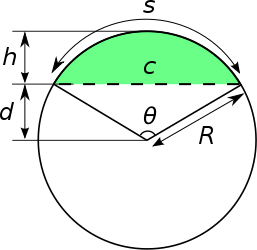
Circular segment
The complete line is known as a secant, and the section inside the disk as a chord.
These can't be calculated simply from chord length and height, so two intermediate quantities, the radius and central angle are usually calculated first.
The radius is: The central angle is The chord length and height can be back-computed from radius and central angle by: The chord length is The sagitta is The apothem is The arc length, from the familiar geometry of a circle, is The area a of the circular segment is equal to the area of the circular sector minus the area of the triangular portion (using the double angle formula to get an equation in terms of
, so a good approximation is a delta offset from the latter area: As an example, the area is one quarter the circle when θ ~ 2.31 radians (132.3°) corresponding to a height of ~59.6% and a chord length of ~183% of the radius.
[clarification needed] The perimeter p is the arclength plus the chord length, As a proportion of the whole area of the disc,
, you have The area formula can be used in calculating the volume of a partially-filled cylindrical tank lying horizontally.
In the design of windows or doors with rounded tops, c and h may be the only known values and can be used to calculate R for the draftsman's compass setting.
One can reconstruct the full dimensions of a complete circular object from fragments by measuring the arc length and the chord length of the fragment.
For calculating the area or locating the centroid of a planar shape that contains circular segments.