Climate change scenario
For example, the IPCC Special Report on Global Warming of 1.5 °C was a "key scientific input" into the 2018 United Nations Climate Change Conference.
The IPCC Sixth Assessment Report defines scenario as follows: "A plausible description of how the future may develop based on a [...] set of assumptions about key driving forces and relationships.
The formal definition of pathways is as follows: "The temporal evolution of natural and/or human systems towards a future state.
Decision makers can use a pathway to make a plan, e.g. with regards to the timing of fossil-fuel phase out or the reduction of fossil fuel subsidies.
There is considerable variety among scenarios, ranging from variants of sustainable development, to the collapse of social, economic, and environmental systems.
[12] The following parameters influence what the scenarios look like: future population levels, economic activity, the structure of governance, social values, and patterns of technological change.
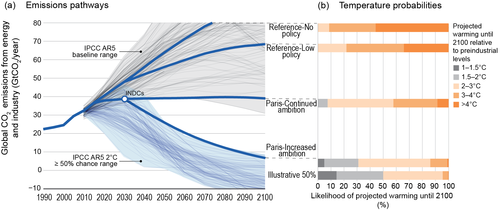
In the majority of studies, the following relationships were found (but are not proof of causation):[12] Predicted trends for greenhouse gas emissions are shown in different formats: Climate change mitigation scenarios are possible futures in which global warming is reduced by deliberate actions, such as a comprehensive switch to energy sources other than fossil fuels.
These are actions that minimize emissions so atmospheric greenhouse gas concentrations are stabilized at levels that restrict the adverse consequences of climate change.
[16] The Paris Agreement has the goal to keep the increase of global temperature below 2 °C, preferably below 1.5 °C above pre-industrial levels to reduce effects of climate change.
Contributions to climate change, whether they cool or warm the Earth, are often described in terms of the radiative forcing or imbalance they introduce to the planet's energy budget.
The BLUE scenarios in the IEA's Energy Technology Perspectives publication of 2008 describe pathways to a long-range concentration of 450 ppm.
The scenario also features, after 2020, the participation of major economies such as China and India in a global cap-and-trade scheme initially operating in OECD and European Union countries.
According to the International Energy Agency (IEA) and OECD, "Achieving lower concentration targets (450 ppm) depends significantly on the use of BECCS".
As approximately a doubling of CO2 levels relative to preindustrial times, it implies a temperature increase of about three degrees, according to conventional estimates of climate sensitivity.
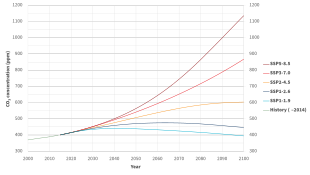
The pathways describe different climate change scenarios, all of which were considered possible depending on the amount of greenhouse gases (GHG) emitted in the years to come.
The lower RCP values, on the other hand, are more desirable for humans but would require more stringent climate change mitigation efforts to achieve them.
[29] A short description of the RCPs is as follows: RCP 1.9 is a pathway that limits global warming to below 1.5 °C, the aspirational goal of the Paris Agreement.
[37] In terms of quantitative elements, they provide data accompanying the scenarios on national population, urbanization and GDP (per capita).
[44] As the spatial resolution of the underlying GCMs is typically quite coarse, the projections are often downscaled, either dynamically using regional climate models (RCMs), or statistically.