Climate system
[1]: 1450 It represents the average weather, typically over a period of 30 years, and is determined by a combination of processes, such as ocean currents and wind patterns.
These external forcings can be natural, such as variations in solar intensity and volcanic eruptions, or caused by humans.
Accumulation of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, mainly being emitted by people burning fossil fuels, is causing climate change.
Not only does the hydrological cycle determine patterns of precipitation, it also has an influence on the movement of energy throughout the climate system.
Most frozen water is contained in the ice sheets on Greenland and Antarctica, which average about 2 kilometres (1.2 miles) in height.
The locations of the seas are important in controlling the transfer of heat and moisture across the globe, and therefore, in determining global climate.
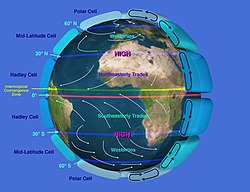
[24] More energy reaches the tropics than the polar regions and the subsequent temperature difference drives the global circulation of the atmosphere and oceans.
[27] Monsoons, seasonal changes in wind and precipitation that occur mostly in the tropics, form due to the fact that land masses heat up more easily than the ocean.
[30] Vertical movements can bring up colder water to the surface in a process called upwelling, which cools down the air above.
[34] The evaporation of water requires substantial quantities of energy, whereas a lot of heat is released during condensation.
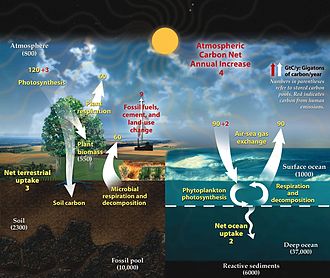
[35] Chemical elements, vital for life, are constantly cycled through the different components of the climate system.
The minerals that are released in this way, transported to the sea, are used by living creatures whose remains can form sedimentary rocks, bringing the carbon back to the lithosphere.
[48] The difference in pressure oscillates and this affects weather patterns across the North Atlantic region up to central Eurasia.
[51] The ocean and atmosphere can also work together to spontaneously generate internal climate variability that can persist for years to decades at a time.
Understanding internal variability helped scientists to attribute recent climate change to greenhouse gases.
[59] Volcanoes, for example, result from deep processes within the earth that are not considered part of the climate system.
Human actions, off-planet changes, such as solar variation and incoming asteroids, are also external to the climate system's five components.
Together these produce Milankovitch cycles, which affect climate and are notable for their correlation to glacial and interglacial periods.
[64] Greenhouse gases trap heat in the lower part of the atmosphere by absorbing longwave radiation.
[65] The dominant contributor to the greenhouse effect is water vapour (~50%), with clouds (~25%) and CO2 (~20%) also playing an important role.
[67] Liquid and solid particles in the atmosphere, collectively named aerosols, have diverse effects on the climate.
[69] Natural sources of aerosols include sea spray, mineral dust, meteorites and volcanoes.
Aerosols counteract some of the warming effects of emitted greenhouse gases until they fall back to the surface in a few years or less.
[71] On average, there are only several volcanic eruptions per century that influence Earth's climate for longer than a year by ejecting tons of SO2 into the stratosphere.
[72][73] The sulfur dioxide is chemically converted into aerosols that cause cooling by blocking a fraction of sunlight to the Earth's surface.
The atmosphere typically responds within a couple of hours to weeks, while the deep ocean and ice sheets take centuries to millennia to reach a new equilibrium.