Clipper (electronics)
In electronics, a clipper is a circuit designed to prevent a signal from exceeding a predetermined reference voltage level.
Clipping circuits are used to select, for purposes of transmission, that part of a signal waveform which lies above or below the predetermined reference voltage level.
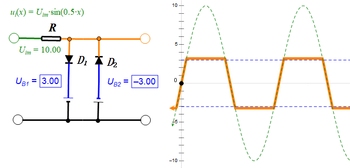
[2] The diode capacitance affects the operation of the clipper at high frequency and influences the choice between the above two types.
High frequency signals are attenuated in the shunt clipper as the diode capacitance provides an alternative path to output current.
In the series clipper, clipping effectiveness is reduced for the same reason as the high frequency current passes through without being sufficiently blocked.
The clipping action can be made to happen at an arbitrary level by using a biasing element (potential source) in series with the diode.