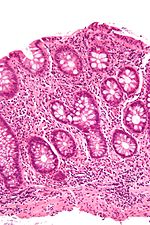
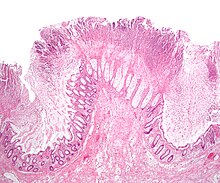
Colitis
[2] Common symptoms of colitis may include: mild to severe abdominal pains and tenderness (depending on the stage of the disease), persistent hemorrhagic diarrhea with pus either present or absent in the stools, fecal incontinence, flatulence, fatigue, loss of appetite and unexplained weight loss.
[3] Other less common or rare non-specific symptoms that may accompany colitis include: arthritis, mouth ulcers, painful, red and swollen skin and irritated, bloodshot eyes.
The use of oral probiotic supplements to modify the composition and behavior of the microbiome has been considered as a possible therapy for both induction and maintenance of remission in people with Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis.
A Cochrane review in 2020 did not find clear evidence of improved remission likelihood, nor lower adverse events, in people with Crohn's disease, following probiotic treatment.
[18] One study reported successfully treating experimental colitis in mice with mesenchymal stem cells.
[19] Additional research was conducted by Huang et al. that analyzed specific genes and biological markers that are associated with the risk of colon cancer development in patients with colitis.
[20] Colitis is common in parts of the world where helminthic colonisation is rare, and uncommon in those areas where most people carry worms.
[25] However, the phase 2 trials had used a different formulation of TSO from the one that had been used in the earlier studies that had shown positive outcomes.