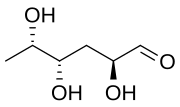
Colitose
[4] The biosynthesis of colitose begins with ColE, a mannose-1-phosphate guanylyltransferase that catalyzes the addition of a GMP moiety to mannose, yielding GDP-mannose.
In the next step, ColB, an NADP-dependent short-chain dehydrogenase-reductase enzyme, catalyzes the oxidation at C-4 and the removal of the hydroxyl group at C-6.
The resulting product, GDP-4-keto-6-deoxymannose, then reacts with the PLP-dependent enzyme GDP-4-keto-6-deoxymannose-3-dehydratase (ColD), which removes the hydroxyl at C-3 in a manner similar to that of serine dehydratase.
In the final step, the product of ColD, GDP-4-keto-3,6-dideoxymannose, reacts with ColC, which reduces the ketone functionality at C-4 back to an alcohol and inverts the configuration about C-5.
ColD is a PLP-dependent enzyme responsible for the removal of the C-3' hydroxyl group during the biosynthesis of GDP-colitose.