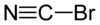Cyanogen bromide
It is a colorless solid that is widely used to modify biopolymers, fragment proteins and peptides (cuts the C-terminus of methionine), and synthesize other compounds.
Cyanogen bromide is often used to immobilize proteins by coupling them to reagents such as agarose for affinity chromatography.
[5] Because of its simplicity and mild pH conditions, cyanogen bromide activation is the most common method for preparing affinity gels.
Cyanogen bromide is also often used because it reacts with the hydroxyl groups on agarose to form cyanate esters and imidocarbonates.
These groups are reacted with primary amines in order to couple the protein onto the agarose matrix, as shown in the figure.
Also, cyanogen bromide activation involves the attachment of a ligand to agarose by an isourea bond, which is positively charged at neutral pH and thus unstable.
[6][dead link] Cyanogen bromide hydrolyzes peptide bonds at the C-terminus of methionine residues.
The electron density in cyanogen bromide is shifted away from the carbon atom, making it unusually electrophilic, and towards the more electronegative bromine and nitrogen.
The strongest electrophile would then be the cyanide carbon, which, if attacked by water, would yield cyanic acid and the original cysteine.
An advantage to HCl is that formic acid causes the formation of formyl esters, which complicates protein characterization.
Alternative buffers for cleavage include guanidine or urea in HCl because of their ability to unfold proteins, thereby making methionine more accessible to BrCN.
Lowered pH tends to increase cleavage rates by inhibiting methionine side chain oxidation.
In most reactions, it acts as a source of electrophilic cyanogen and nucleophilic bromide; carbocations preferentially attack the nitrogen atom.