Genetic testing
[10] Genetic testing is "the analysis of chromosomes (DNA), proteins, and certain metabolites in order to detect heritable disease-related genotypes, mutations, phenotypes, or karyotypes for clinical purposes.
For example, a medical procedure called a buccal smear uses a small brush or cotton swab to collect a sample of cells from the inside surface of the cheek.
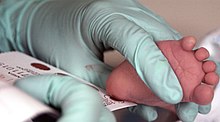
[citation needed] Routine newborn screening tests are done on a small blood sample obtained by pricking the baby's heel with a lancet.
The procedures used for prenatal testing carry a small but non-negligible risk of losing the pregnancy (miscarriage) because they require a sample of amniotic fluid or tissue from around the fetus.
Some individuals avoid genetic testing out of fear it will affect their ability to purchase insurance or find a job.
[31] DNA studies have been criticised for a range of methodological problems and providing misleading, interpretations on racial classifications.
These companies will send the consumer a kit at their home address, with which they will provide a saliva sample for their lab to analyze.
The company will then send back the consumer's results in a few weeks, which is a breakdown of their ancestral heritage and possible health risks that accompany it.
Without professional guidance, consumers can potentially misinterpret genetic information, causing them to be deluded about their personal health.
An advertisement for a BRCA-predictive genetic test for breast cancer stated: "There is no stronger antidote for fear than information.
"[47] Ancestry.com, a company providing DTC DNA tests for genealogy purposes, has reportedly allowed the warrantless search of their database by police investigating a murder.
[50] The aim is to minimise health problems by warning participants most at risk of conditions such as cardiovascular disease and diabetes.
Over one million people participated in the DNA sampling from more than 140 countries, which made the project the largest of its kind ever conducted.
The legislation also bars employers from using genetic information when making hiring, firing, job placement, or promotion decisions.
[64] Direct-to-consumer (DTC) genetic tests, especially those for health-related purposes, are prohibited unless conducted with medical oversight to ensure informed consent and appropriate counseling.
Within the framework of this program, it is also planned to include the peoples of neighboring countries, which are the main source of migration, into the genogeographic study on the basis of existing collections.
[67] By the end of 2021, the UAE Genome Project will be in full swing, as part of the National Innovation Strategy, establishing strategic partnerships with top medical research centers, and making sustainable investments in healthcare services.
Additionally, a study by Khalifa University has identified, for the first time, four genetic markers associated with type 2 diabetes among UAE citizens.
[69][70] Under the Genetic Information Law as of 2019, commercial DNA tests are not permitted to be sold directly to the public, but can be obtained with a court order, due to data privacy, reliability, and misinterpretation concerns.
Guidelines also state that parents or guardians should be encouraged to inform their child of the results from the genetic test if the minor is of appropriate age.
Within the guidelines set by AAP and ACMG, health care providers have an obligation to inform parents or guardians on the implication of test results.
[75][76][77][78] From the date that a sample is taken, results may take weeks to months, depending upon the complexity and extent of the tests being performed.
This article incorporates public domain material from What is the cost of genetic testing, and how long does it take to get the results?.