Stem cell
[1] Research into stem cells grew out of findings by Canadian biologists Ernest McCulloch, James Till and Andrew J. Becker at the University of Toronto and the Ontario Cancer Institute in the 1960s.
[8] Pioneering works in theory of blood stem cell were conducted in the beginning of 20th century by Artur Pappenheim, Alexander A. Maximow, Franz Ernst Christian Neumann.
[8] The key properties of a stem cell were first defined by Ernest McCulloch and James Till at the University of Toronto and the Ontario Cancer Institute in the early 1960s.
In subsequent work, McCulloch and Till, joined by graduate student Andrew John Becker and senior scientist Louis Siminovitch, confirmed that each lump did in fact arise from a single cell.
[9] The first therapy using stem cells was a bone marrow transplant performed by French oncologist Georges Mathé in 1956 on five workers at the Vinča Nuclear Institute in Yugoslavia who had been affected by a criticality accident.
[10] In 1981, embryonic stem (ES) cells were first isolated and successfully cultured using mouse blastocysts by British biologists Martin Evans and Matthew Kaufman.
This allowed the formation of murine genetic models, a system in which the genes of mice are deleted or altered in order to study their function in pathology.
In 2006, Shinya Yamanaka's team in Kyoto, Japan converted fibroblasts into pluripotent stem cells by modifying the expression of only four genes.
These cells transition to a neurogenic state and start to divide asymmetrically to produce a large diversity of many different neuron types, each with unique gene expression, morphological, and functional characteristics.
The radial glial cell, has a distinctive bipolar morphology with highly elongated processes spanning the thickness of the neural tube wall.
Mouse ES cells are grown on a layer of gelatin as an extracellular matrix (for support) and require the presence of leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF) in serum media.
The transcription factors Oct-4, Nanog, and Sox2 form the core regulatory network that ensures the suppression of genes that lead to differentiation and the maintenance of pluripotency.
MSC can differentiate into numerous cell categories as an illustration of adipocytes, osteocytes, and chondrocytes, derived by the mesodermal layer.
The term "meso" means middle, infusion originated from the Greek, signifying that mesenchymal cells are able to range and travel in early embryonic growth among the ectodermal and endodermal layers.
This mechanism helps with space-filling thus, key for repairing wounds in adult organisms that have to do with mesenchymal cells in the dermis (skin), bone, or muscle.
Although the exact molecular mechanism remains only partially understood, several studies have shown insight on how ESCs progress through G1—and potentially other phases—so rapidly.
Also similar to mESCs, hESCs demonstrate the importance of Cdk2 in G1 phase regulation by showing that G1 to S transition is delayed when Cdk2 activity is inhibited and G1 is arrest when Cdk2 is knocked down.
[citation needed] Pluripotent adult stem cells are rare and generally small in number, but they can be found in umbilical cord blood and other tissues.
[48] Bone marrow is a rich source of adult stem cells,[49] which have been used in treating several conditions including liver cirrhosis,[50] chronic limb ischemia[51] and endstage heart failure.
[58] Adult stem cell treatments have been successfully used for many years to treat leukemia and related bone/blood cancers through bone marrow transplants.
Additionally, in instances where adult stem cells are obtained from the intended recipient (an autograft), the risk of rejection is essentially non-existent.
[63] Several factors appear to influence HSC aging including responses to the production of reactive oxygen species that may cause DNA damage and genetic mutations as well as altered epigenetic profiling.
[78] Junying Yu, James Thomson, and their colleagues at the University of Wisconsin–Madison used a different set of factors, Oct4, Sox2, Nanog and Lin28, and carried out their experiments using cells from human foreskin.
As a result of the success of these experiments, Ian Wilmut, who helped create the first cloned animal Dolly the Sheep, has announced that he will abandon somatic cell nuclear transfer as an avenue of research.
By providing a suitable scaffold and microenvironment, iPSC can be differentiated into cells of therapeutic application, and for in vitro models to study toxins and pathogenesis.
[76] Moreover, unlike ESCs, they potentially could allow doctors to create a pluripotent stem cell line for each individual patient.
[83] Patient specific stem cells allow for the screening for side effects before drug treatment, as well as the reduced risk of transplantation rejection.
[90] The National Institutes of Health (NIH) Guidelines on Human Stem Cell Research, effective July 7, 2009, implemented the Executive Order 13505 by establishing criteria which hESC lines must meet to be approved for funding.
[96] For over 50 years, hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) has been used to treat people with conditions such as leukaemia and lymphoma; this is the only widely practiced form of stem-cell therapy.
[122] At a hearing in December 2013, the CAFC raised the question of whether Consumer Watchdog had legal standing to appeal; the case could not proceed until that issue was resolved.
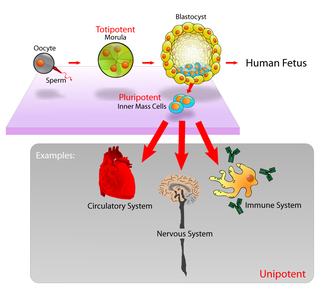

A: Stem cell colonies that are not yet differentiated.
B: Nerve cells, an example of a cell type after differentiation.


