Data editing
[4] Editing methods refer to a range of procedures and processes which are used for detecting and handling errors in data.
These modifications can greatly improve the quality of analytics created by aiming to detect and correct errors.
[5] Interactive editing reduces the time frame needed to complete the cyclical process of review and adjustment.
Selective editing is an umbrella term for several methods to identify the influential errors, [note 1] and outliers.
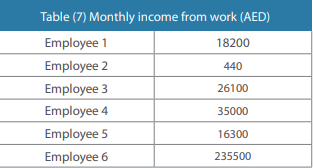
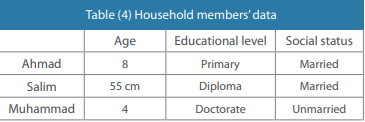
One method of data editing is to ensure that all responses are complete in fields that require a numerical or non-numerical answer.
The values can be considered erroneous and require further analysis for checking and determining the validity of the response.
This editing requires a certain understanding around the dataset and the ability to identify errors in data based on previous reports or information.
If an unusual value is observed, a micro-editing procedure is applied to the individual records and fields contributing to the suspicious quantity.
Records containing values that could be considered uncommon (given the distribution) are candidates for further inspection and possibly for editing.