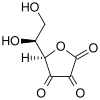
Dehydroascorbic acid
Recycling of vitamin C via active transport of DHA into cells, followed by reduction and reuse, mitigates the inability of humans to synthesize it from glucose.
[6] Vitamin C accumulates in mitochondria, where most of the free radicals are produced, by entering as DHA through the glucose transporter GLUT10.
[13] As a pharmaceutical agent, some research has suggested that administration of dehydroascorbic acid may confer protection from neuronal injury following an ischemic stroke.
[16][17] A pharmaceutical product named Ascoxal is an example of such a solution used as a mouth rinse as an oral mucolytic and prophylactic agent against gingivitis.
[17][18] Ascoxal solution has also been tested with positive results as a treatment for recurrent mucocutaneous herpes,[18] and as a mucolytic agent in acute and chronic pulmonary disease such as emphysema, bronchitis, and asthma by aerosol inhalation.