Social behavior
This means that, in regards to humans, social behavior can be determined by both the individual characteristics of the person, and the situation they are in.
[7] Social behavior constantly changes as one continues to grow and develop, reaching different stages of life.
What takes particular precedence in the influence of the setting are the people that the child must interact with their age, sex, and at times culture.
[7] Emotions also play a large role in the development of social behavior, as they are intertwined with the way an individual behaves.
Through social interactions, emotion is understood through various verbal and nonverbal displays, and thus plays a large role in communication.
The development of social behavior is influenced by their mothers' reactions to children's emotional displays.
[8] Once the individual reaches child rearing age, one must begin to undergo changes within the own behavior in accordance to major life-changes of a developing family.
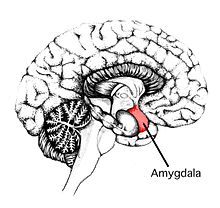
The medial prefrontal lobe has also been seen to have activation during social cognition[13] Research has discovered through studies on rhesus monkeys that the amygdala, a region known for expressing fear, was activated specifically when the monkeys were faced with a social situation they had never encountered before.
Lesions in the prefrontal cortex that occurred in adulthood can affect the functioning of social behavior.
When these lesions or a dysfunction in the prefrontal cortex occur in infancy/early on in life, the development of proper moral and social behavior is effected and thus atypical.
[15] Along with neural correlates, research has investigated what happens within the body (and potentially modulates) social behavior.
Vasopressin is a posterior pituitary hormone that is seen to potentially play a role in affiliation for young rats.
Thus, targeting levels of oxytocin may play a role in interventions of disorders that deal with atypical social behavior.
[18] Studies have shown that even subtly inducing positive affect within individuals caused greater social behavior and helping.
However, with the advent of electronic media, people began to find themselves in situations they may have not been exposed to in everyday life.
This has led to a cascade of results, as gender norms started to merge, and people were coming in contact with information they had never been exposed to through face-to-face interaction.
The general learning model was established to study how this process of translating media into behavior works, and why.
This model also presents the notion that when one is exposed to the same type of media for long periods of time, this could even lead to changes within their personality traits, as they are forming different sets of knowledge and may be behaving accordingly.
[29][30] When these songs were played at restaurants, it even led to an increase in tips given (relative to those who heard neutral lyrics).
[32] Generally speaking, the larger the group size, the easier it is for individuals to display conformity behaviors.
[39] Gestures (coverbal behaviors) and speech occur simultaneously, and develop along the same trajectory within children as well.
Due to this pervasive fear of embarrassing oneself in front of others, it causes those affected to avoid interactions with other people.