Dependency network
The dependency network approach provides a system level analysis of the activity and topology of directed networks.
The approach extracts causal topological relations between the network's nodes (when the network structure is analyzed), and provides an important step towards inference of causal activity relations between the network nodes (when analyzing the network activity).
This methodology has originally been introduced for the study of financial data,[1][2] it has been extended and applied to other systems, such as the immune system,[3] semantic networks,[4] and functional brain networks.
[5][6][7] In the case of network activity, the analysis is based on partial correlations.
This results in a directed weighted adjacency matrix of a fully connected network.
Once the adjacency matrix has been constructed, different algorithms can be used to construct the network, such as a threshold network, Minimal Spanning Tree (MST), Planar Maximally Filtered Graph (PMFG), and others.
The partial correlation based dependency network is a class of correlation network, capable of uncovering hidden relationships between its nodes.
This original methodology was first presented at the end of 2010, published in PLoS ONE.
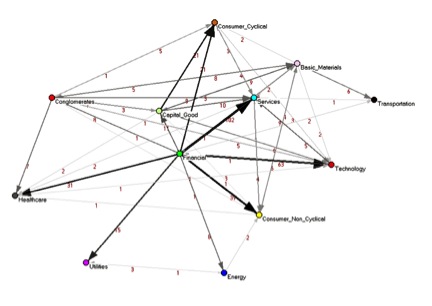
[1] The authors quantitatively uncovered hidden information about the underlying structure of the U.S. stock market, information that was not present in the standard correlation networks.
One of the main results of this work is that for the investigated time period (2001–2003), the structure of the network was dominated by companies belonging to the financial sector, which are the hubs in the dependency network.
Thus, they were able for the first time to quantitatively show the dependency relationships between the different economic sectors.
In the case of network topology, the analysis is based on the effect of node deletion on the shortest paths between the network nodes.
are the activity of nodes i and j of subject n, μ stands for average, and sigma the STD of the dynamics profiles of nodes i and j.
The first order partial correlation coefficient is a statistical measure indicating how a third variable affects the correlation between two other variables.
of node j on the correlation C(i,k) is given by: This avoids the trivial case were node j appears to strongly affect the correlation
For this reason, some of the methods used in the analyses of the correlation matrix (e.g. the PCA) have to be replaced or are less efficient.
Yet there are other methods, as the ones used here, that can properly account for the non-symmetric nature of the dependency matrix.
– the shortest topological path with each segment corresponds to a distance 1, between nodes i and k is given: where
It is important to note that the dependency matrix D is nonsymmetrical –
Different algorithms can be applied to filter the fully connected network to obtain the most meaningful information, such as using a threshold approach,[1] or different pruning algorithms.
A widely used method to construct informative sub-graph of a complete network is the Minimum Spanning Tree (MST).
[13][14][15][16][17] Another informative sub-graph, which retains more information (in comparison to the MST) is the Planar Maximally Filtered Graph (PMFG)[18] which is used here.
Both methods are based on hierarchical clustering and the resulting sub-graphs include all the N nodes in the network whose edges represent the most relevant association correlations.
edges with no loops while the PMFG sub-graph contains