Diethylamine
[5] Diethylamine is used in the production of corrosion inhibitor N,N-diethylaminoethanol, by reaction with ethylene oxide.
[6] As the most abundantly available secondary amine that is liquid at room temperature, diethylamine has been extensively deployed in chemical synthesis.
It participates in Mannich reactions involving the installation of diethylaminomethyl substituents.
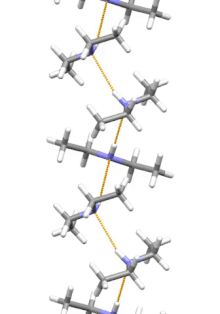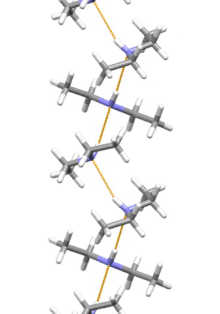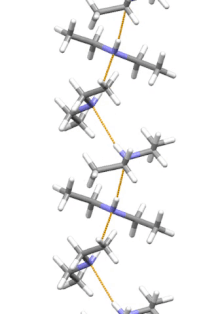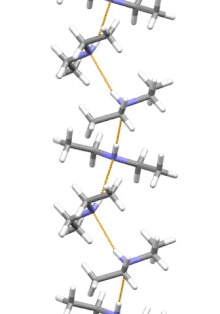
[11] Diethylamine is the smallest and simplest molecule that features a supramolecular helix as its lowest energy aggregate.
[12] Diethylamine has low toxicity, but the vapor causes transient impairment of vision.