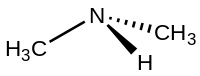
Dimethylamine
Dimethylamine is a weak base and the pKa of the ammonium CH3-NH+2-CH3 is 10.73, a value above methylamine (10.64) and trimethylamine (9.79).
Dimethylamine is produced by catalytic reaction of methanol and ammonia at elevated temperatures and high pressure:[6] Dimethylamine is found quite widely distributed in animals and plants, and is present in many foods at the level of a few mg/kg.
[5][8] It reacts with carbon disulfide to give dimethyl dithiocarbamate, a precursor to zinc bis(dimethyldithiocarbamate) and other chemicals used in the sulfur vulcanization of rubber.
The surfactant lauryl dimethylamine oxide is found in soaps and cleaning compounds.
For example reaction of dimethylamine and formaldehyde gives bis(dimethylamino)methane:[15] It converts esters to dimethylamides.
[16] Although not acutely toxic, dimethylamine undergoes nitrosation to give dimethylnitrosamine, a carcinogen.