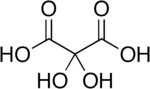
Dihydroxymalonic acid
Dihydroxymalonic acid is an organic compound with formula C3H4O6 or HO-(C=O)-C(OH)2-(C=O)-OH, found in some plants such as alfalfa and in beet molasses.
[3] This compound is unusual in containing stable geminal hydroxy groups.
[4] It has been used in medical research as a hypoglycemic agent[5] and was patented in the United States in 1997 as a fast-acting antidote to cyanide poisoning.
The product can be obtained also by oxidation of tartronic acid [9] or glycerol.
By continued boiling of its aqueous solution it is decomposed into carbon dioxide and glyoxylic acid.