East Antarctic Shield
Because the surface of the shield is covered by ice and therefore not directly accessible, the information about its tectonic history comes primarily from seismic and core-sample data.
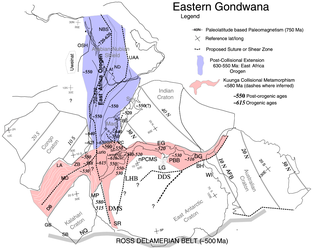
[2] However, it has been determined that the East Antarctic Shield has a Precambrian to Ordovician basement of igneous and sedimentary rocks that are deformed and metamorphosed to varying degrees, and intruded by syn- to post-tectonic granites.
This was taken as evidence for a continuous, late Mesoproterozoic to early Neoproterozoic mobile belt skirting across the coast of the East Antarctic Shield.
[9] These sediments were deposited at a passive margin that likely developed during the rifting of North America from the East Antarctic Shield, and were subsequently deformed and metamorphosed at a low- to medium-grade and intruded by syn- and post-tectonic granitoids.
Tectonism was relatively synchronous between the two from 550 to 515 Ma and both belts overprinted late Mesoproterozoic to early Neoproterozoic, Grenville-age magmatic and metamorphosed rocks.
[11] Further evidence for ocean closure along the Lutzow Holm Belt is provided by the different ages of Grenville-age tectonism in the Maud and Rayner Provinces of either side of the inferred suture.
The climax of activity in both the Lutzow Holm and Prydz Belts was at 530 Ma, but the possibility of two-near-simultaneous collisions cannot be discounted and would mean that East Antarctica comprise three major crustal fragments that did not combine until the Cambrian.
[13] Pangea ruptured during the Jurassic, preceded by and associated with widespread magmatic activity, including the Karoo flood basalts and related dyke swarms in South Africa and the Ferrar Province in East Antarctica.
[17] Relative extension between West Australia and East Antarctica commenced in the Late Cretaceous to Early Tertiary, but oceanic crust between these two plates was formed only between 45 and 30 Ma in the Adare Trough of the Ross Sea.