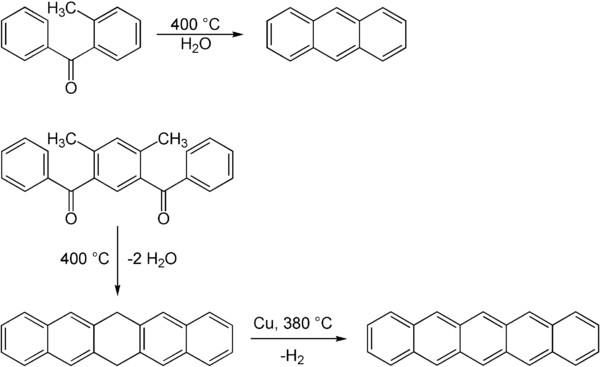
Elbs reaction
[1][2][3] Elbs however did not correctly interpret the reaction product due to a lack of knowledge about naphthalene structure.
The Elbs reaction enables the synthesis of condensed aromatic systems.
[2][4] The Elbs reaction is sometimes accompanied by elimination of substituents and can be unsuited for substituted polyaromatics.
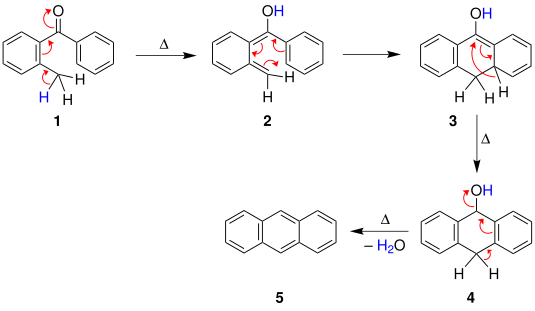
[5] The first mechanism, suggested by Fieser, begins with a heat-induced cyclisation of the benzophenone, followed by a [1,3]-hydride shift to give the compound .
Alternatively, in the second mechanism, due to Cook, the methylated aromatic compound instead first undergoes a tautomerization followed by an electrocyclic reaction to give the same intermediate, which then similarly undergoes a [1,3]-hydride shift and dehydration.