Electron optics
The term optics is used because magnetic and electrostatic lenses act upon a charged particle beam similarly to optical lenses upon a light beam.
In the paraxial approximation, trajectory calculations can be carried out using ray transfer matrix analysis.
Electrons can be accelerated by suitable electric fields, thereby acquiring kinetic energy.
[1]: 745 This index of refraction functions like the material properties of glass in altering the direction ray propagation.
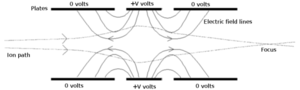
In the electron-optics, the index varies throughout space and is controlled by electromagnetic fields created outside the electron trajectories.
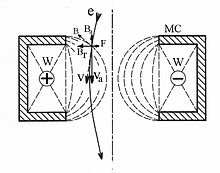
In an infinite uniform field this results in a circular motion of the electron around the field direction with a radius given by: where r is the orbit radius, m is the mass of an electron,
Electrons that have a velocity component parallel to the magnetic field will proceed along helical trajectories.
Although not very common, it is also possible to derive effects of magnetic structures to charged particles starting from the Dirac equation.
Free electron propagation (in vacuum) can be accurately described as a de Broglie matter wave with a wavelength inversely proportional to its longitudinal (possibly relativistic) momentum.
Fortunately as long as the electromagnetic field traversed by the electron changes only slowly compared with this wavelength (see typical values in matter wave#Applications of matter waves), Kirchhoff's diffraction formula applies.
[1] The essential character of this approach is to use geometrical ray tracing but to keep track of the wave phase along each path to compute the intensity in the diffraction pattern.
As a result of the charge carried by the electron, electric fields, magnetic fields, or the electrostatic mean inner potential of thin, weakly interacting materials can impart a phase shift to the wavefront of an electron.
Penetration in vacuum is dictated by mean free path, a measure of the probability of collision between electrons and matter, approximate values for which can be derived from Poisson statistics.