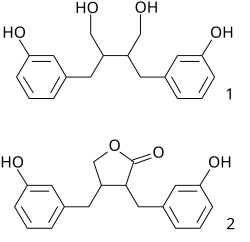
Enterolignan
Enterolignans are organic compounds formed by the action of gut microflora on lignans.
They are thus the products of the combined action of both plants and of the animal gut.
[1] Enterolignans have attracted intense attention because of their potential beneficial roles in nutrition.
Elevated levels of enterodiol in urine are attributed consumption of tea and other lignan-rich foods.
[1][2] This article about an aromatic compound is a stub.