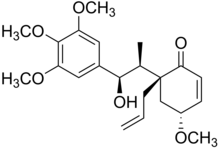
Megaphone (molecule)
Megaphone is a cytotoxic neolignan obtained from Aniba megaphylla, a flowering plant in the laurel family which gave the compound its name.
[1][2][3] Studies carried out in the 1960s demonstrated that an alcoholic extract of the ground root of Aniba megaphylla inhibited, in vitro, growth of cells derived from human carcinoma of the nasopharynx.
In 1978, the active components of the extract were isolated using silica gel chromatography, characterized and named as megaphone (C22H30O6, solid), megaphone acetate (C24H32O7, oily liquid) and megaphyllone acetate (C23H28O7, oily liquid).
[4] Megaphone acetate was also isolated from the root of Endlicheria dysodantha, another plant of Laurel family, using chromatography of ethanolic solution.
It showed inhibitory activity against cells of crown gall tumor and human lung, breast and colon carcinomas.