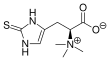
Ergothioneine
Ergothioneine is a naturally occurring amino acid and is a thiourea derivative of histidine, containing a sulfur atom on the imidazole ring.
[5][6] In humans, ergothioneine is acquired exclusively through the diet and accumulates in erythrocytes, bone marrow, liver, kidney, seminal fluid, and eyes.
In the human body, the largest amounts of ergothioneine are found in erythrocytes, eye lens, semen,[6] and skin.
[16] Other species of bacteria, such as Bacillus subtilis, Escherichia coli, Proteus vulgaris, and Streptococcus, as well as fungi in the Saccharomycotina cannot make ergothioneine.
[1][7] The Panel on Dietetic Products for the European Food Safety Authority reported safe daily limits of 2.82 mg/kg of body weight for infants, 3.39 mg/kg for small children, and 1.31 mg/kg for adults, including pregnant and breastfeeding women.