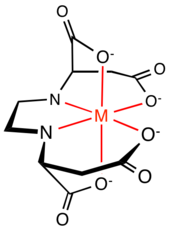
EDDS
It is a colourless solid that is used as chelating agent that may offer a biodegradable alternative to EDTA, which is currently used on a large scale in numerous applications.
In comparing the effectiveness of (S,S)-EDDS versus EDTA as chelating agents for iron(III): Because of the lower stability for [Fe(S,S)-EDDS]−, the useful range being roughly 3 (S,S)-EDDS is a biodegradable chelating agent that offers an alternative to EDTA, of which 80 million kilograms are produced annually. Under natural conditions, EDTA has been found to convert to ethylenediaminetriacetic acid and then cyclize to the diketopiperazine, which accumulates in the environment as a persistent organic pollutant. [10] When EDDS is applied in chemical-enhanced soil remediation in excessive case (e.g., when applied for ex-situ soil washing), higher extraction efficiency for heavy metals can be achieved and the amount of extraction is less independent with the EDDS dosage;[11] On the other hand, during soil remediation which involves continuous flushing, metal extraction is often limited by the amount of EDDS.