Fatty acid degradation
[1][2] It includes three major steps: Initially in the process of degradation, fatty acids are stored in adipocytes.
The products of lipolysis, free fatty acids, are released into the bloodstream and circulate throughout the body.
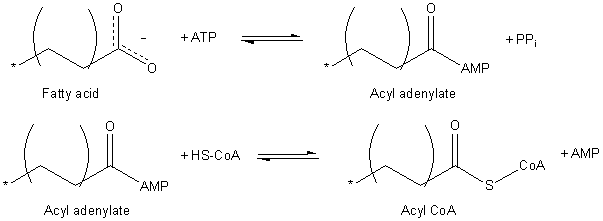
The enzyme first catalyzes nucleophilic attack on the α-phosphate of ATP to form pyrophosphate and an acyl chain linked to AMP.
The balanced equation for the above is: RCOO− + CoASH + ATP → RCO-SCoA + AMP + PPi This two-step reaction is freely reversible and its equilibrium lies near 1.
This occurs via a series of similar steps: Carnitine acyltransferase I undergoes allosteric inhibition as a result of malonyl-CoA, an intermediate in fatty acid biosynthesis, in order to prevent futile cycling between beta-oxidation and fatty acid synthesis.