Flavin group
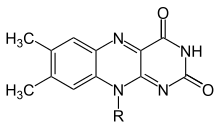
Flavins (from Latin flavus, "yellow") refers generally to the class of organic compounds containing the tricyclic heterocycle isoalloxazine or its isomer alloxazine, and derivatives thereof.
Reduction is made with the addition of hydrogen atoms to specific nitrogen atoms on the isoalloxazine ring system: In aqueous solution, flavins are yellow-coloured when oxidized, taking a red colour in the semi-reduced anionic state or blue in the neutral (semiquinone) state, and colourless when totally reduced.
For example, the LOV domain, found in many species of plant, fungi and bacteria, undergoes a reversible, light-dependent structural change which involves the formation of a bond between a cysteine residue in its peptide sequence and a bound FMN.
FADH2 is produced as a prosthetic group in succinate dehydrogenase, an enzyme involved in the citric acid cycle.
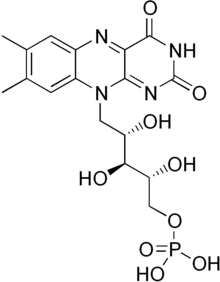
Flavin mononucleotide is a prosthetic group found in, among other proteins, NADH dehydrogenase, E.coli nitroreductase and old yellow enzyme.