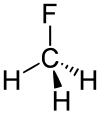
Fluoromethane
Methyl fluoride Halocarbon 41 0.557 g/cm3 (liquid) at saturation pressure at 25 °C Fluoromethane, also known as methyl fluoride, Freon 41, Halocarbon-41 and HFC-41, is a non-toxic, liquefiable, and flammable gas at standard temperature and pressure.
[2] Fluoromethane (originally called "fluorohydrate of methylene") became the first organofluorine compound to be discovered[3] when it was synthesized by French chemists Jean-Baptiste Dumas and Eugène-Melchior Péligot in 1835 by distilling dimethyl sulfate with potassium fluoride.
These compounds are related to the chlorofluorocarbons (CFC), but since they do not contain chlorine, are not destructive to the ozone layer.
[5] Fluorocarbons are, however, potent greenhouse gasses, and the Kigali Amendment to the Montreal Protocol is an attempt to phase them out due to their contribution to global warming.
Its Dipole Moment is 1.85 D.[citation needed] Its specific heat capacity (Cp) is 38.171 J·mol−1·K−1 at 25 °C.