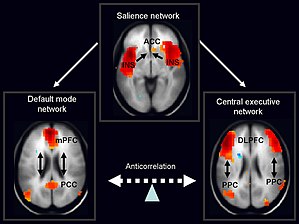
Frontoparietal network
[1][2] The FPN is primarily composed of the rostral lateral and dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (especially the middle frontal gyrus) and the anterior inferior parietal lobule.
Additional regions include the middle cingulate gyrus and potentially the dorsal precuneus, posterior inferior temporal lobe, dorsomedial thalamus and the head of the caudate nucleus.
[7] The FPN is involved in executive function and goal-oriented, cognitively demanding tasks.
[7] It is crucial for rule-based problem solving, actively maintaining and manipulating information in working memory and making decisions in the context of goal-directed behaviour.
[8] Disruption of the nodes of the FPN has been found in virtually every psychiatric and neurological disorder, from autism, schizophrenia and depression to frontotemporal dementia and Alzheimer's disease.