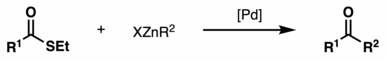
Fukuyama coupling
In particular, the protocol is compatible with sensitive functional groups such as ketones, α-acetates, sulfides, aryl bromides, chlorides, and aldehydes.
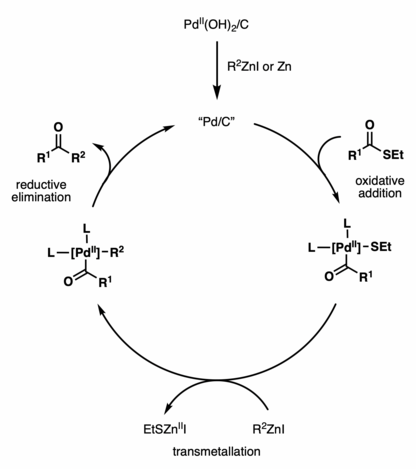
[3] The active Pd/C species then undergoes oxidative addition with a thioester, followed by transmetallation with a zinc reagent and reductive elimination, to afford the ketone coupling product.
[4] Remarkably, α−amino ketones starting from thioester derivatives of N-protected amino acids can be synthesized without racemization in good to excellent yields (58-88%).
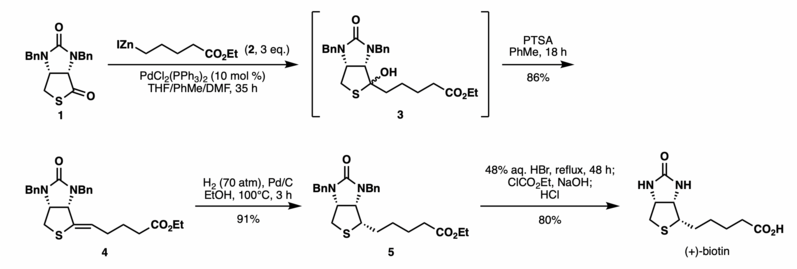
Shimizu and Seki realized the efficient synthesis of (+)-biotin via the Fukuyama coupling of the thiolactone 1 and an easily prepared alkyl zinc reagent 2 in the presence of catalytic PdCl2(PPh3)2.
The reaction generated an alcohol 3 which was directly reacted without purification with PTSA to afford alkene 4 in 86% yield as a single isomer.