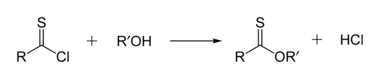
Thioester
[4] Efforts to improve the sustainability of thioester synthesis have also been reported utilising safer coupling reagent T3P and greener solvent cyclopentanone.
Thioesters are common intermediates in many biosynthetic reactions, including the formation and degradation of fatty acids and mevalonate, precursor to steroids.
The biosynthesis of lignin, which comprises a large fraction of the Earth's land biomass, proceeds via a thioester derivative of caffeic acid.
Oxidation of the sulfur atom in thioesters (thiolactones) is postulated in the bioactivation of the antithrombotic prodrugs ticlopidine, clopidogrel, and prasugrel.
[14] As Christian de Duve explains: It is revealing that thioesters are obligatory intermediates in several key processes in which ATP is either used or regenerated.
They also participate in the synthesis of a number of other cellular components, including peptides, fatty acids, sterols, terpenes, porphyrins, and others.
Eventually, [these] thioesters could have served to usher in ATP through its ability to support the formation of bonds between phosphate groups.However, due to the high free energy change of thioester's hydrolysis and correspondingly their low equilibrium constants, it is unlikely that these compounds could have accumulated abiotically to any significant extent especially in hydrothermal vent conditions.